Investing in the stock market is one of the most powerful ways to build long-term wealth and financial independence. Whether you are a beginner investor or a professional looking to improve your investment skills, understanding stock market fundamentals is the first step toward achieving consistent success. The stock market provides opportunities to grow capital, earn passive income, and own shares in some of the world’s most successful companies.

This comprehensive guide will introduce essential stock market concepts, explain how stocks create wealth, and provide practical strategies used by professional investors to build strong investment portfolios.
Understanding Risk and the Rules of Investing
Before entering the stock market, every investor must understand the importance of risk management. Legendary investor Warren Buffett once said that the first rule of investing is “Don’t lose money,” and the second rule is “Never forget the first rule.” These principles emphasize capital preservation and disciplined decision-making.

Successful investing is not about quick profits or speculation. Instead, it requires patience, knowledge, and a clear understanding of the businesses you invest in. Investors should only invest in companies they understand and focus on long-term growth rather than short-term market fluctuations. The best investment you can make is in yourself—by learning financial knowledge and improving your investment skills, you increase your potential to earn more over time.
What Is the Stock Market?
The stock market is a place where investors buy and sell shares of publicly listed companies. It functions like a marketplace where businesses offer ownership shares to raise capital and investors purchase those shares to participate in company growth and profits.

Think of the stock market as a global supermarket of businesses. Every day, shares of companies are available at different prices based on supply, demand, and company performance. By buying stocks, investors become partial owners of companies and benefit from their success without the need to start or manage a business themselves.
The stock market allows individuals to own shares in global companies such as technology firms, financial institutions, and consumer brands. Investors can earn returns through capital appreciation—when stock prices rise—and through dividends, which are payments made by companies to shareholders from their profits.
What Is a Share of Stock?
A share of stock represents ownership in a company. When you buy shares, you own a portion of the business and have the right to participate in its profits. For example, if a company has one million shares and you own ten thousand shares, you own one percent of the company.
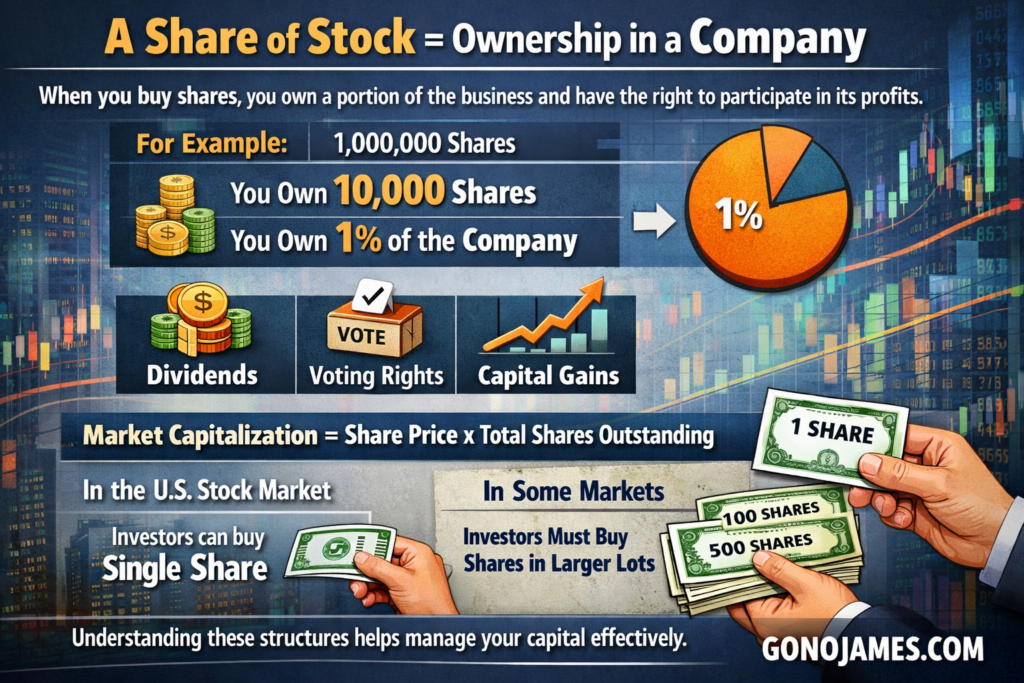
Shareholders may receive dividends, voting rights, and capital gains when stock prices increase. The value of a company in the market is called market capitalization, which is calculated by multiplying the share price by the total number of shares outstanding.
In the United States stock market, investors can buy even a single share, making it accessible to everyone. However, in some markets, investors must buy shares in larger quantities called lots. Understanding these structures helps investors plan their strategies and manage their capital effectively.
Fundamental Analysis and Stock Valuation
Fundamental analysis is one of the most important tools for long-term investors. It involves analyzing a company’s financial health, earnings, growth potential, and competitive position to determine whether its stock is undervalued or overvalued.

One of the most commonly used valuation metrics is the Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio. The P/E ratio measures how much investors are willing to pay for each dollar of a company’s earnings. It is calculated by dividing the stock price by earnings per share (EPS). A high P/E ratio may indicate that a stock is expensive or that investors expect strong future growth. A low P/E ratio may suggest a stock is undervalued or facing challenges.
Investors also analyze revenue growth, profit margins, and return on equity to evaluate company performance. When a company consistently increases its profits and revenue, its stock price often rises over time. Strong financial fundamentals provide a foundation for long-term investment success.
Stock Buybacks and Dividends
Companies create value for shareholders in several ways, including dividends and stock buybacks. Dividends are direct payments to shareholders from company profits, providing passive income for investors. Many long-term investors seek dividend-paying stocks for consistent income.

Stock buybacks occur when a company uses its cash to repurchase its own shares from the market. This reduces the number of shares outstanding and increases earnings per share. When EPS increases, the value of each remaining share may rise, benefiting shareholders. Buybacks signal that management believes the company’s stock is undervalued and worth investing in.
Stock Splits and Accessibility
Stock splits occur when a company divides its shares to make them more affordable for investors. For example, in a 10-for-1 stock split, each shareholder receives ten shares for every one share they own, while the price per share decreases proportionally. Although the total value of the investment remains the same, stock splits make shares more accessible and often attract new investors.

Major companies like Apple and Nvidia have implemented stock splits to maintain liquidity and encourage broader participation in their stocks. While stock splits do not change a company’s fundamental value, they can increase market interest and trading activity.
Why Invest in the US Stock Market?
The US stock market is considered one of the strongest and most stable financial markets in the world. Major indices such as the S&P 500 and Nasdaq have demonstrated long-term growth, driven by innovation, technology, and global economic leadership.

Many of the world’s most successful companies are listed in the United States, offering investors access to high-quality businesses with strong growth potential. Historically, the US market has delivered consistent returns over the long term, making it attractive for global investors seeking wealth creation and portfolio diversification.
How Stocks Build Wealth
Stocks build wealth through two main mechanisms: capital appreciation and dividends. Capital appreciation occurs when the value of a stock increases over time due to company growth and improved financial performance. Dividends provide regular income and can be reinvested to compound returns.
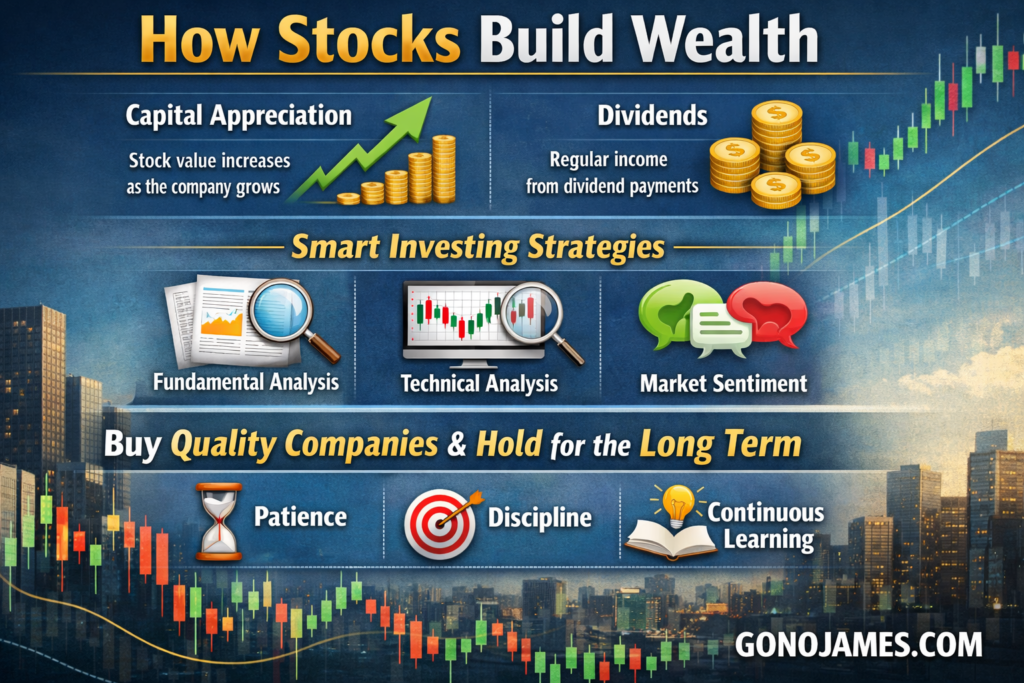
Successful investors combine fundamental analysis, technical analysis, and market sentiment to make informed decisions. They focus on buying quality companies at reasonable prices and holding them for the long term. Patience, discipline, and continuous learning are essential for achieving consistent investment success.
Final Thoughts
The stock market offers unlimited opportunities for those willing to learn and invest wisely. By understanding stock market basics, analyzing company fundamentals, and building diversified portfolios, investors can create sustainable wealth and financial freedom.
Whether you are just starting your investment journey or seeking advanced strategies, mastering stock market fundamentals is the key to long-term success. Invest in knowledge, stay disciplined, and focus on quality investments to achieve your financial goals in the global stock market.